Data Types
There are two forms of datatypes in Java:
- Primitive data type
- Non-Primitive data type
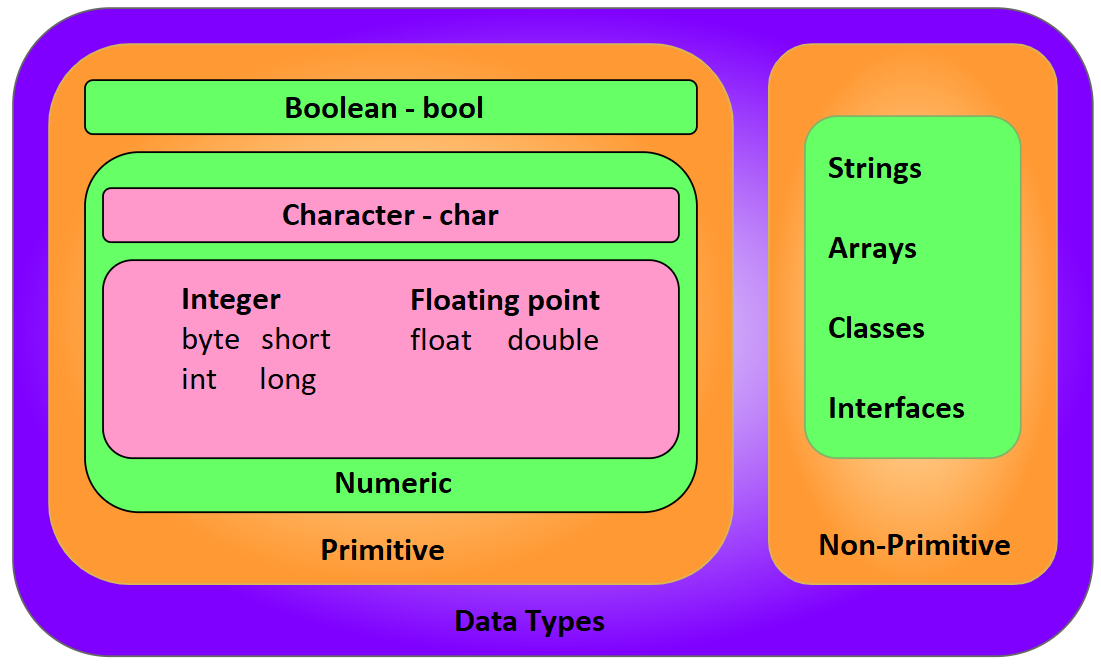
- bool: Boolean data type consists of true and false values.
- char: char datatype is used to store characters.
- byte: The main purpose of byte is to save memory and consists of values in the range -128 to 127.
- short: Consists of values in the range -32768 to 32767.
- int: Consists of values in the range -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
- long: Consists of values in the range -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807.
- float: Can be used to deal with decimal numbers. Always recommended to use float rather than double because float saves memory.
- double: Can be used to deal with decimal numbers.
| Data Type | Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| bool | 1 bit | true, false |
| char | 2 byte | a…z, A…Z |
| byte | 1 byte | -27 to 27-1 (-128 to 127) |
| short | 2 byte | -215 to 215-1 (-32768 to 32767) |
| int | 4 byte | -231 to 231-1 (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647) |
| long | 8 byte | -263 to 263-1 (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807) |
| float | 4 byte | 6.022f |
| double | 8 byte | 3.142 |