Inheritance
Inheritance is the mechanism by which one class acquires the properties and features of another class. The class that inherits the properties is called a sub-class (child class) while the class from which the property is inherited is called the super-class (parent class).
A child class inherits properties of the parent class with the help of the extends keyword.
Syntax:
class childClass extends parentClass {
// any code
}Inheritance can be further divided into the following types:
- Single level
- Multi-level
- Hierarchical
- Multiple
- Hybrid
Multiple and hybrid inheritance is not directly supported in Java, instead, it is achieved through the use of interfaces in Java.
i. Single Inheritance
When a single class inherits the attributes and methods of another class, it is known as single inheritance.
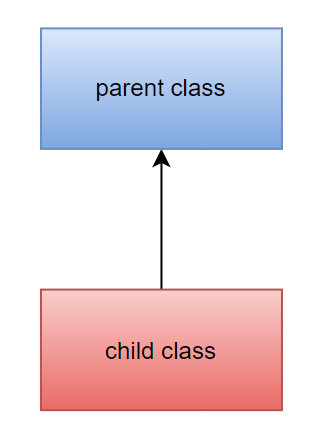
Example:
class FundamentalForce {
void Force() {
System.out.println("There are four fundamental forces.");
}
}
class Gravitational extends FundamentalForce {
void Gravity() {
System.out.println("Fruits fall to the ground due to gravitational Force.");
}
}
class SingleInheritance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gravitational G = new Gravitational();
G.Force();
G.Gravity();
}
}Output:
There are four fundamental forces.
Fruits fall to the ground due to gravitational Force.
In this example, we see how class Gravitational can inherit the method of its parent class (FundamentalForce). This is a perfect example of a parent-child relationship.
ii. Multi-level Inheritance
When a class 3 inherits attributes and methods from class 2 which in turn inherits its attributes and methods from class 1, it is called multi-level inheritance.
It forms a child-parent-grandparent (or a parent-child-grandchild) relationship. Meaning that the child inherits from the parent while the parent inherits from the grandparent.
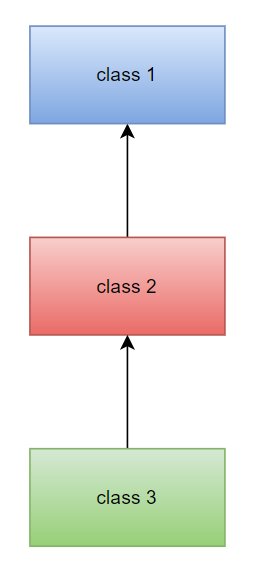
Example:
class NuclearForce extends FundamentalForce {
void Nuclear() {
System.out.println("Nuclear Forces are of two types;");
System.out.println("Strong Nuclear Force");
System.out.println("Weak Nuclear Force");
}
}
class StrongNuclearForce extends NuclearForce {
void Strong() {
System.out.println("Strong Nuclear Force is responsible for the underlying stability of matter.");
}
}
class MultilevelInheritance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StrongNuclearForce st = new StrongNuclearForce();
st.Force();
st.Nuclear();
st.Strong();
}
}Output:
There are four fundamental forces.
Nuclear Forces are of two types;
Strong Nuclear Force
Weak Nuclear Force
Strong Nuclear Force is responsible for the underlying stability of matter.
In this example, we see how class StrongNuclearForce inherits the method of NuclearForce which in turn inherits the method of FundamentalForce. This is a classic example of a child-parent-grandparent relationship.
iii. Hierarchical Inheritance
Hierarchical inheritance is when two or more classes inherit from a single class. This can be easily visualized as a parent with more than one child. Here each child can inherit the properties of a parent.
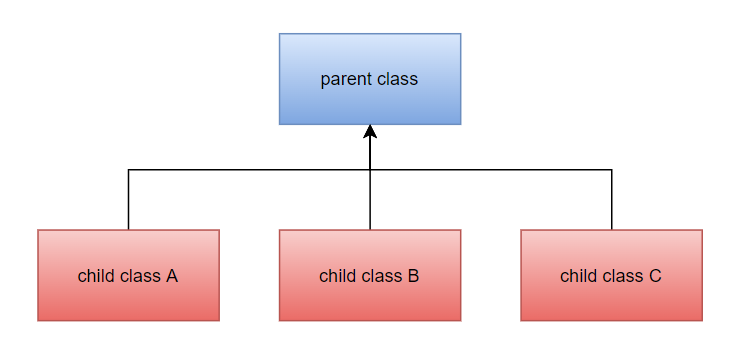
Example:
class FundamentalForce {
void Force() {
System.out.println("There are four fundamental forces.");
}
}
class Gravitational extends FundamentalForce {
void Gravity() {
System.out.println("Fruits fall to the ground due to gravitational Force.");
}
}
class Electromagnetic extends FundamentalForce {
void Particles() {
System.out.println("The electromagnetic force acts between charged particles");
}
}
class HierarchicalInheritance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Child 1:");
Gravitational G = new Gravitational();
G.Force();
G.Gravity();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Child 2");
Electromagnetic em = new Electromagnetic();
em.Force();
em.Particles();
}
}Output:
Child 1:
There are four fundamental forces.
Fruits fall to the ground due to gravitational Force.
Child 2
There are four fundamental forces.
The electromagnetic force acts between charged particles
As we can see, both the children can access the method of the parent class.