Combinators
In CSS, combinators define the relationship between two or more selectors. They allow you to target elements based on their hierarchical or sibling relationship in the HTML structure.
There are 4 main combinators in CSS:
- Descendant Selector (space)
- Child Selector (>)
- Adjacent Sibling Selector (+)
- General Sibling Selector (~)
Let’s go through each of them one by one with examples.
1. Descendant Selector (space)
It selects all the elements present inside another specified HTML element.
Syntax:
A B {
/* styles */
}
Here, B is selected only if it’s inside A (at any depth).
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Descendant Selector Example</title>
<style>
div p {
color: white;
background-color: teal;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Descendant Selector Example</h2>
<div>
<p>Paragraph 1 inside div</p>
<p>Paragraph 2 inside div</p>
<section>
<p>Paragraph 3 nested inside section (still inside div)</p>
</section>
<p>Paragraph 4 inside div</p>
</div>
<p>Paragraph outside div</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
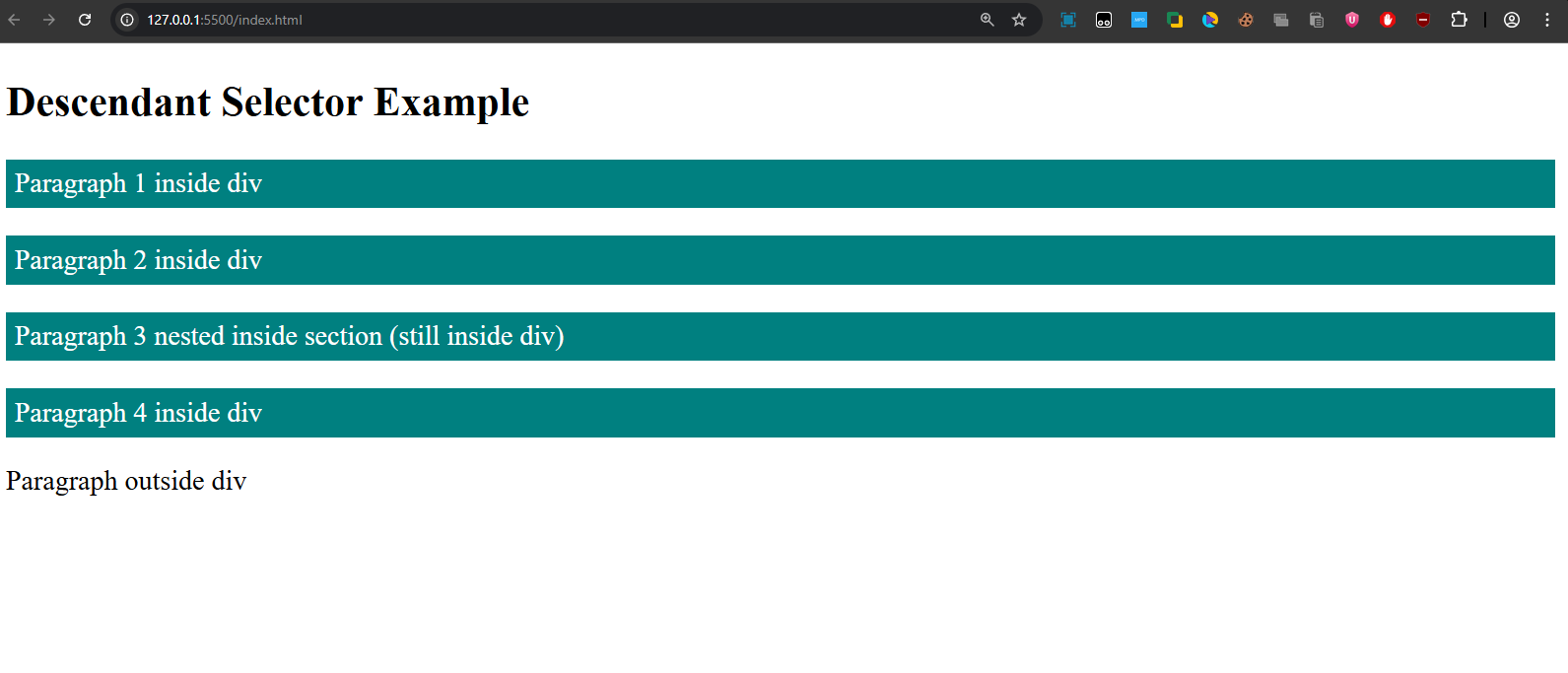
- All
<p>elements inside the<div>are styled. - Even the paragraph inside
<section>is affected, because it’s still inside the<div>. - The last paragraph (outside the
<div>) is not styled.
2. Child Selector (>)
It selects only the first generation descendants of a specified element.
Syntax:
A > B {
/* styles */
}
Here, only the first-generation children of A that match B will be styled.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Child Selector Example</title>
<style>
div > p {
color: white;
background-color: purple;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Child Selector Example</h2>
<div>
<p>Paragraph 1 inside div (direct child)</p>
<p>Paragraph 2 inside div (direct child)</p>
<section>
<p>Paragraph 3 nested inside section (NOT direct child)</p>
</section>
<p>Paragraph 4 inside div (direct child)</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
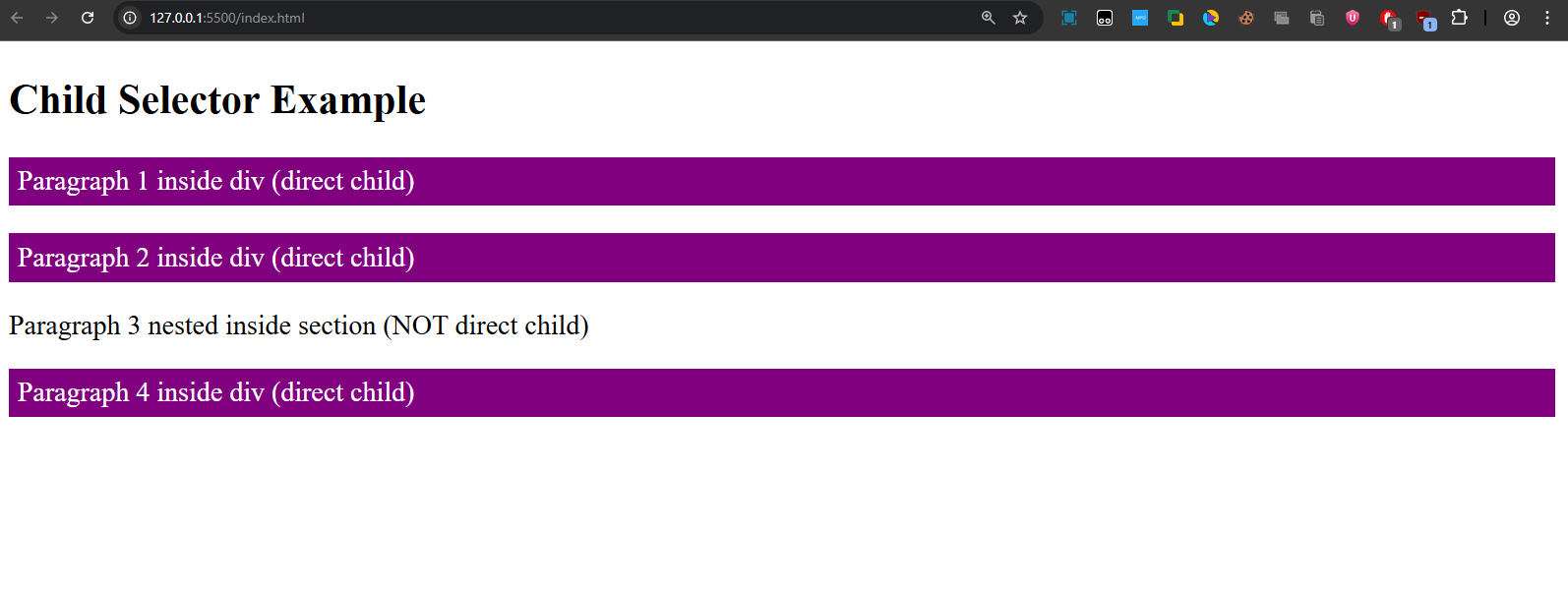
- Paragraphs 1, 2, and 4 are styled (direct children of
<div>). - Paragraph 3 (inside
<section>) is not styled, since it’s a grandchild of<div>.
3. Adjacent Sibling Selector (+)
As the name suggests this selector only selects the adjacent element to the specified element.
Syntax:
A + B {
/* styles */
}
Here, B will be styled only if it comes right after A in the HTML.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Adjacent Sibling Selector Example</title>
<style>
div + p {
color: white;
background-color: darkorange;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Adjacent Sibling Selector Example</h2>
<div>
<p>Paragraph inside div</p>
</div>
<p>Paragraph immediately after div (selected)</p>
<p>Another paragraph (NOT selected)</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
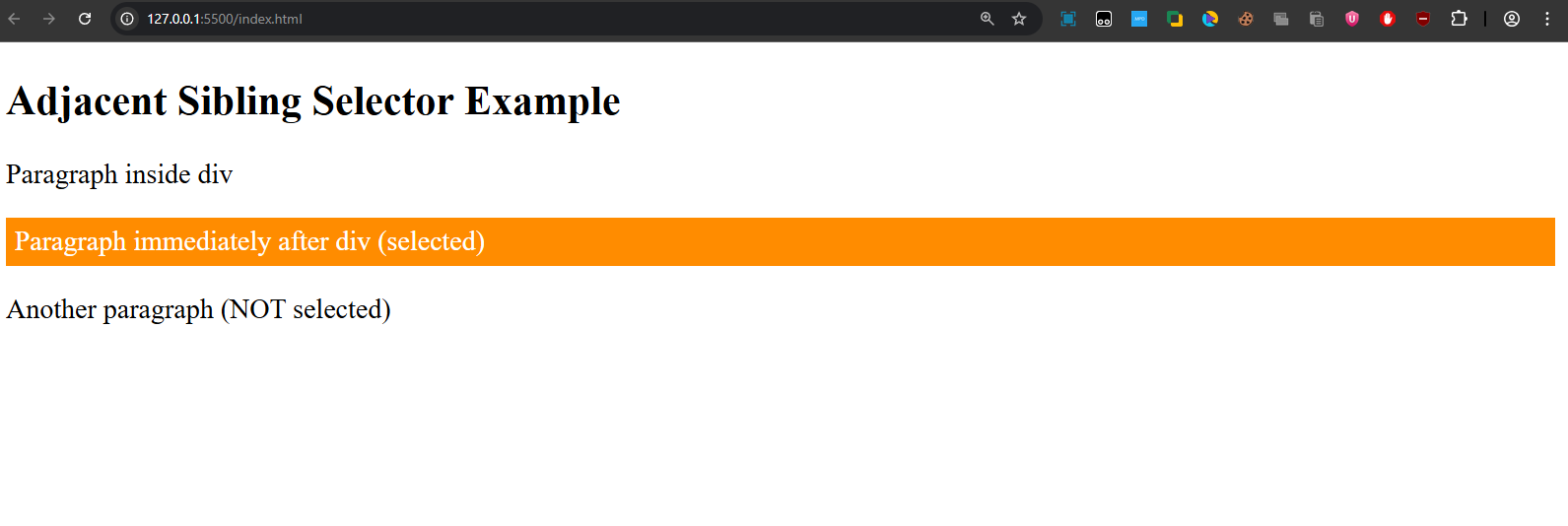
- The first
<p>after the<div>is styled. - Any other paragraphs after that are ignored.
4. General Sibling Selector (~)
The general sibling selector selects all siblings of an element that appear after it in the HTML.
Syntax:
A ~ B {
/* styles */
}
Here, all B elements that are siblings of A and come after it will be styled.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>General Sibling Selector Example</title>
<style>
div ~ p {
color: white;
background-color: seagreen;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>General Sibling Selector Example</h2>
<div>
<p>Paragraph inside div</p>
</div>
<p>Paragraph after div (selected)</p>
<p>Another paragraph after div (also selected)</p>
<p>Yet another paragraph after div (also selected)</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
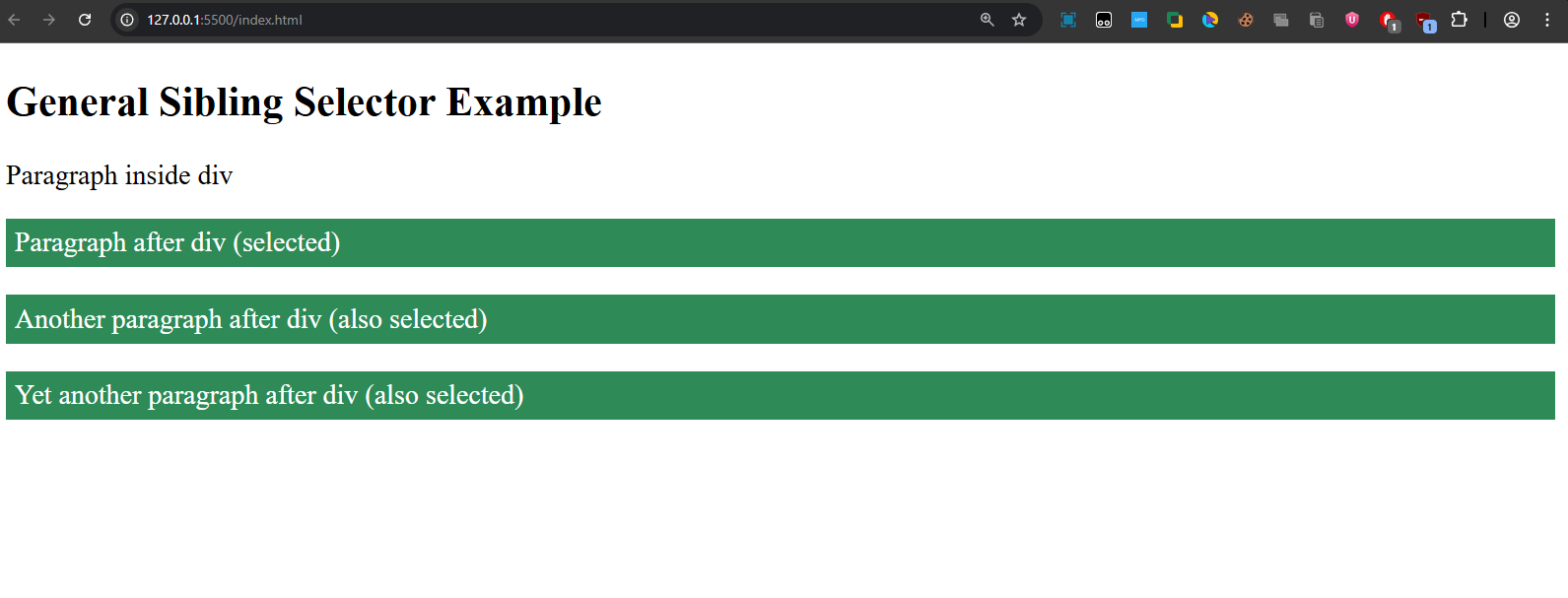
- All
<p>elements that come after the<div>(on the same level) are styled. - The
<p>inside<div>is not affected.
Quick Recap
- Descendant ( ) → Selects all nested elements.
- Child (>) → Selects only direct children.
- Adjacent Sibling (+) → Selects the very next sibling.
- General Sibling (~) → Selects all following siblings.